Decision Tree |
A decision tree is a graph that uses a branching method to illustrate every possible outcome of a decision. Decision tree learning is one of the most successful techniques for supervised classification learning.
The library contains a non-parametric decision tree learning technique Classification and Regression Tree algorithms implementation [Breiman84] .
Decision trees are formed by a collection of rules based on variables in the modeling data set:
Rules based on variables' values are selected to get the best split to differentiate observations based on the dependent variable.
Once a rule is selected and splits a node into two, the same process is applied to each "child" node (i.e. it is a recursive procedure).
Splitting stops when CART detects no further gain can be made, or some pre-set stopping rules are met. (Alternatively, the data are split as much as possible and then the tree is later pruned.)
Each branch of the tree ends in a terminal node. Each observation falls into one and exactly one terminal node, and each terminal node is uniquely defined by a set of rules.
To reach a leaf node and to obtain a response for the input feature vector, the prediction procedure starts with the root node. From each non-leaf node the procedure goes to the left (selects the left child node as the next observed node) or to the right based on the value of a certain variable whose index is stored in the observed node. The following variables are possible:
Ordered variables (DecisionTreeContinuousNode and DecisionTreeContinuousEdge classes). The variable value is compared with a threshold that is also stored in the node. If the value is less than the threshold, the procedure goes to the left. Otherwise, it goes to the right. For example, if the weight is less than 1 kilogram, the procedure goes to the left, else to the right.
Categorical variables (DecisionTreeCategoricalNode and DecisionTreeCategoricalEdge classes). A discrete variable value is tested to see whether it belongs to a certain subset of values (also stored in the node) from a limited set of values the variable could take. If it does, the procedure goes to the left. Otherwise, it goes to the right. For example, if the color is green or red, go to the left, else to the right.
The tree is built recursively, starting from the root node. All training data (feature vectors and responses) is used to split the root node. In each node the optimum decision rule (the best “primary” split) is found based on some criteria. In machine learning, Gini “purity” criteria are used for classification, and sum of squared errors is used for regression. Then, the procedure recursively splits both left and right nodes. At each node the recursive procedure may stop (that is, stop splitting the node further) in one of the following cases:
Depth of the constructed tree branch has reached the specified maximum value.
Number of training samples in the node is less than the specified threshold when it is not statistically representative to split the node further.
All the samples in the node belong to the same class.
The best found split does not give any noticeable improvement compared to a random choice.
When the tree is built, it may be pruned using a cross-validation procedure, if necessary. That is, some branches of the tree that may lead to the model overfitting are cut off.
From the view of space division the decision three is the piecewise linear space separation with hyperplanes parallels to axis. Let’s consider next small decision tree building example on the well know Fisher Iris dataset ( http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/Iris).
The DecisionTree class allows build soft or harsh pruned trees. On the next figure you can see hard pruned nodes (with white background color and solid borders) and soft pruned nodes (with gray background color and dashed borders).
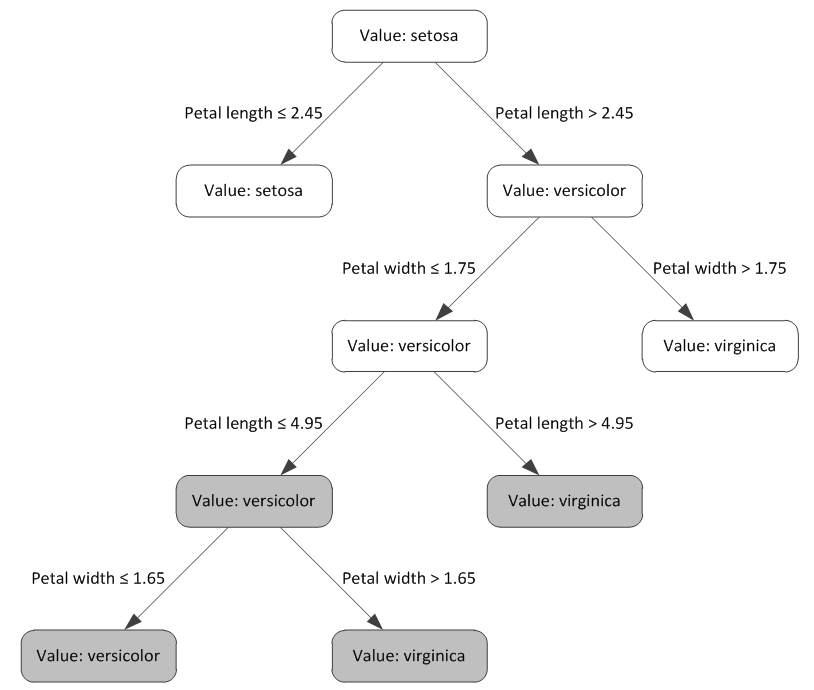
As you can see, every decision node (not only leafs) contains the prediction value. This value will be used as the prediction value if all the sub-tree will be cut.
Well known, the sepal length is highly correlated with petal length and sepal width is highly correlated with petal width. So, in most cases the iris data set can be efficiently classified and displayed only in two uncorrelated dimensions. The decision tree boundaries in coordinates of petal length and petal width are displayed on the next figure.
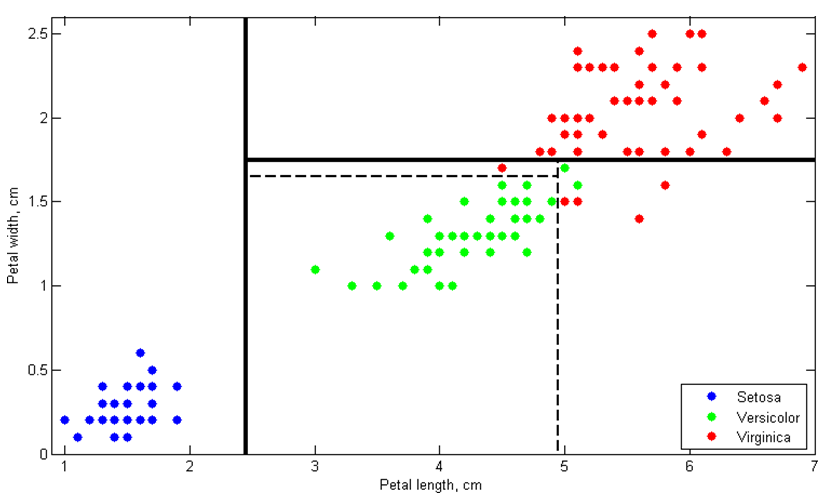
To create the DecisionTree instance use the following constructors:
Constructor | Description | Performance |
|---|---|---|
create DecisionTree instance | The Decision tree default constructor. | |
create DecisionTree instance | Creates the decision tree from other sub-tree
|
The following methods are featured in DecisionTree class:
Method | Description | Performance |
|---|---|---|
save | Save model to files. | |
load | Load model from files. | |
train | Build decision tree function. | |
classify | Classifies observation vector/matrix into one of the classes. |
The following constructors serve to create instances of Categorical/Continuous Edge/Node:
Constructor | Description | Performance |
|---|---|---|
categorical edge | Categorical edge constructor. | |
continuous edge | Continuous edge constructor. | |
categorical node | Categorical node constructor. | |
continuous node | Continuous node constructor. |
The DecisionTree class allows to not only enumerate the nodes and edges of the tree, but also allows to edit tree:
create new tree from some node of the source tree - use the constructor with source tree as a parameter;
chop the sub-tree from specified node - use method
 Chop;
Chop;graft the sub-tree as child of some node - use the methods below:
Method | Description | Performance |
|---|---|---|
graft | Graft sub-tree as this node sub-nodes for categorical/continuous node. |
This allows user to modify tree at his own discretion.
The example of SVM Classification usage:
1using System; 2using FinMath.LinearAlgebra; 3using FinMath.DataStructures; 4using FinMath.MachineLearning; 5using System.Collections.Generic; 6// using System.Linq; 7 8namespace FinMath.Samples 9{ 10 class DecisionTreeSample 11 { 12 /// <summary> 13 /// Knuth shuffle 14 /// </summary> 15 static void Shuffle(Random r, Matrix X, IntegerArray a) 16 { 17 int n = a.Length; 18 int t_a; 19 Vector t_X; 20 while (n > 0) 21 { 22 int i = r.Next(n); 23 n--; 24 t_a = a[i]; 25 a[i] = a[n]; 26 a[n] = t_a; 27 t_X = X.GetRow(i); 28 X.SetRow(i, X.GetRow(n)); 29 X.SetRow(n, t_X); 30 } 31 } 32 33 static void AVShow(DecisionTree.BaseNode node, string s) 34 { 35 if (node.IsLeaf) 36 { 37 Console.WriteLine($"{s}Leaf {node.Prediction} {node}"); 38 return; 39 } 40 if (node is DecisionTree.ContinuousNode) 41 { 42 DecisionTree.ContinuousNode connode = node as DecisionTree.ContinuousNode; 43 foreach (DecisionTree.ContinuousEdge edge in connode) 44 { 45 Console.WriteLine($"{s}ContiniousEdge {connode.FactorIndex}: {edge.LeftBoundary} - {edge.RightBoundary}"); 46 AVShow(edge.NodeTo, s + "\t"); 47 } 48 } 49 else 50 { 51 DecisionTree.CategoricalNode catnode = node as DecisionTree.CategoricalNode; 52 foreach (DecisionTree.CategoricalEdge edge in catnode) 53 { 54 Console.Write($"{s}CategoricalEdge {catnode.FactorIndex}: "); 55 for (Int32 i = 0; i < edge.AcceptableCategories.Count; ++i) 56 Console.Write(" " + edge.AcceptableCategories[i]); 57 Console.WriteLine(); 58 AVShow(edge.NodeTo, s + "\t"); 59 } 60 } 61 } 62 63 static void AVTest() 64 { 65 int observationCount = 3000; 66 int continuesFactorCount = 5; 67 int categoricalFactorCount = 5; 68 Random r = new Random(/*(int)DateTime.Now.Ticks*/123); 69 Matrix X = Matrix.Random(observationCount, continuesFactorCount + categoricalFactorCount, r); 70 IntegerArray a = new IntegerArray(observationCount); 71 List<DecisionTree.FactorType> factorType = new List<DecisionTree.FactorType>(categoricalFactorCount + continuesFactorCount); 72 73 for (int i = 0; i < continuesFactorCount; ++i) 74 factorType.Add(DecisionTree.FactorType.Continuous); 75 76 for (int i = 0; i < categoricalFactorCount; ++i) 77 factorType.Add(DecisionTree.FactorType.Categorical); 78 79 for (int i = 0; i < observationCount; ++i) 80 { 81 for (int j = 0; j < categoricalFactorCount; ++j) 82 { 83 X[i, j + continuesFactorCount] = r.Next(3); 84 } 85 86 if (X[i, continuesFactorCount + 3] == 2 || X[i, continuesFactorCount + 3] == 0) 87 { 88 if (X[i, 3] < 0.5) 89 a[i] = 0; 90 else 91 a[i] = 1; 92 93 } 94 else 95 { 96 if (X[i, 1] < 0.8) 97 a[i] = 2; 98 else 99 a[i] = 3; 100 } 101 } 102 103 Vector priors = new Vector(new Double[] { 0.1954, 0.2120, 0.2491, 1.0000 }); 104 105 Shuffle(r, X, a); 106 107 X.Save(@"av_x.csv"); 108 a.Save(@"av_a.csv"); 109 110 DecisionTree tree = new DecisionTree(); 111 Console.WriteLine("Train"); 112 tree.Train(X, a, factorTypes: factorType, doPrune: false); 113 114 tree.Save(@"av_tree_unpraned.xml"); 115 116 tree.Train(X, a, factorTypes: factorType); 117 118 tree.Save(@"av_tree_praned.xml"); 119 120 AVShow(tree.Root, ""); 121 } 122 123 static void XORTest() 124 { 125 Matrix x = new Matrix(1000, 2); 126 IntegerArray c = new IntegerArray(x.Rows); 127 128 for (int i = 0; i < x.Rows; ++i) 129 { 130 Double rho = (Double)i / x.Rows; 131 Double theta = i; 132 x[i, 0] = rho * Math.Cos(theta); 133 x[i, 1] = rho * Math.Sin(theta); 134 c[i] = x[i, 0] * x[i, 1] > 0 ? 1 : -1; 135 } 136 137 Shuffle(new Random(123), x, c); 138 139 x.Save("xor_x.csv"); 140 c.Save("xor_c.csv"); 141 142 DecisionTree tree = new DecisionTree(); 143 tree.Train(x, c, useOneSERule: true); 144 145 tree.Save("xor_model.xml"); 146 147 AVShow(tree.Root, ""); 148 } 149 150 static void Main() 151 { 152 XORTest(); 153 154 RandnTest(); 155 156 AVTest(); 157 158 ADTest(); 159 } 160 161 static void LoadIris(String filename, out Matrix meas, out IntegerArray species) 162 { 163 String[] lines = System.IO.File.ReadAllLines(filename); 164 if (lines.Length < 1) 165 throw new Exception("Can't read input file " + filename); 166 167 int rows_number = 0, first_nonempty = int.MaxValue; 168 for (int i = 0; i < lines.Length; ++i) 169 if (lines[i].Length != 0) 170 { 171 rows_number++; 172 first_nonempty = Math.Min(first_nonempty, i); 173 } 174 175 if (rows_number == 0) 176 throw new Exception("There are no date in this file."); 177 178 string[] words = lines[first_nonempty].Split(','); 179 180 meas = new Matrix(rows_number, words.Length - 1); 181 species = new IntegerArray(rows_number); 182 183 Dictionary<String, Int32> species_list = new Dictionary<String, Int32>(); 184 185 for (int i = 0, k = 0; i < lines.Length; ++i, ++k) 186 { 187 if (lines[i].Length == 0) 188 { 189 --k; 190 continue; 191 } 192 193 words = lines[i].Split(','); 194 195 if (words.Length != meas.Columns + 1) 196 throw new Exception("Can't parse " + i + 1 + " line in file " + filename); 197 198 for (int j = 0; j < meas.Columns; ++j) 199 meas[k, j] = Double.Parse(words[j]); 200 201 if (!species_list.ContainsKey(words[meas.Columns])) 202 species_list.Add(words[meas.Columns], species_list.Count + 1); 203 204 species[k] = species_list[words[meas.Columns]]; 205 } 206 } 207 208 static void RandnTest() 209 { 210 Matrix observations; 211 IntegerArray categories; 212 213 LoadIris(@"iris.data", out observations, out categories); 214 215 DecisionTree dtree = new DecisionTree(); 216 217 Shuffle(new Random(), observations, categories); 218 219 dtree.Train(observations, categories, useOneSERule: true, doPrune: true); 220 221 ADDispTree(dtree.Root); 222 223 dtree.Save(@"fi_tree_pruned.xml"); 224 225 dtree.Train(observations, categories, useOneSERule: false, doPrune: true); 226 227 dtree.Save(@"fi_tree_pruned_unharsh.xml"); 228 229 dtree.Train(observations, categories, useOneSERule: false, doPrune: false); 230 231 dtree.Save(@"fi_tree_unpraned.xml"); 232 } 233 234 235 static void ADTest() 236 { 237 DecisionTree dtree = new DecisionTree(); 238 239 { 240 Matrix observations = new Matrix(200, 2); 241 IntegerArray categories = new IntegerArray(observations.Rows); 242 243 for (int i = 0; i < observations.Rows; ++i) 244 { 245 bool is_class1 = i < (observations.Rows / 2); 246 247 categories[i] = is_class1 ? -1 : 1; 248 249 if (is_class1) 250 { 251 Double t = (Double)i * 2.5 / (observations.Rows / 2.0) - 1.0; 252 observations[i, 0] = Math.Round(3 * t); 253 observations[i, 1] = Math.Abs(t); 254 } 255 else 256 { 257 Double t = 2.5 * ((Double)i / (observations.Rows / 2.0) - 1.0) - 1.0; 258 observations[i, 0] = Math.Round(3 * (-t - 1)); 259 observations[i, 1] = 1.5 - Math.Abs(t); 260 } 261 } 262 263 List<DecisionTree.FactorType> types = new List<DecisionTree.FactorType>(); 264 types.AddRange(new DecisionTree.FactorType[] { DecisionTree.FactorType.Categorical, DecisionTree.FactorType.Continuous }); 265 266 //Vector priors = new Vector(10); 267 //for (int i = 0; i < priors.Count; ++i) 268 // priors[i] = (i + 1) / 100.0; 269 270 // Train|Predict example 271 272 Shuffle(new Random(), observations, categories); 273 274 dtree.Train(observations, categories, factorTypes: types, minimumObservationsNumber: 2, 275 numFoldsPruning: 10, useOneSERule: false, doPrune: true); 276 277 observations.Save(@"ad_x.csv"); 278 categories.Save(@"ad_a.csv"); 279 280 dtree.Save(@"ad_tree_pruned.xml"); 281 282 dtree.Train(observations, categories, factorTypes: types, minimumObservationsNumber: 2, 283 numFoldsPruning: 10, useOneSERule: false, doPrune: false); 284 285 dtree.Save(@"ad_tree_unpruned.xml"); 286 287 Int32 category = dtree.Classify((Vector)(new double[] { 0, 0.55 })); 288 289 IntegerArray categories1 = new IntegerArray(observations.Rows); 290 for (int i = 0; i < observations.Rows; ++i) 291 categories1[i] = dtree.Classify(observations.GetRow(i)); 292 293 294 string filename = "tree.xml"; 295 // Save|Load example 296 dtree.Save(filename); 297 298 dtree = new DecisionTree(); 299 dtree.Load(filename); 300 301 observations.Save(filename + ".observations.csv"); 302 } 303 304 305 ADDispTree(dtree.Root); 306 307 308 // Editing example 309 { 310 DecisionTree dtree2 = new DecisionTree((DecisionTree.BaseNode)dtree.Root.Clone(), dtree.ClassList); 311 312 dtree2.Save("tree_node_root.xml"); 313 314 int i = 0; 315 foreach (DecisionTree.BaseEdge edge in dtree2.Root) 316 (new DecisionTree((DecisionTree.BaseNode)edge.NodeTo.Clone(), dtree2.ClassList)).Save($"tree_node_{i++}.xml"); 317 318 while (true) 319 { 320 IEnumerator<DecisionTree.BaseEdge> edge_it = dtree2.Root.GetEnumerator(); 321 if (!edge_it.MoveNext()) 322 break; 323 edge_it.Current.NodeTo.Chop(); 324 } 325 326 dtree2.Save("tree_choop.xml"); 327 328 DecisionTree.BaseNode r0 = dtree.Root; 329 DecisionTree.BaseNode r1 = dtree2.Root; 330 331 foreach (DecisionTree.BaseEdge edge in dtree.Root) 332 { 333 if (edge is DecisionTree.ContinuousEdge) 334 { 335 if (dtree2.Root.GetType() != typeof(DecisionTree.ContinuousNode)) 336 dtree2.Root.Replace(new DecisionTree.ContinuousNode(0 /*factor index*/, -1 /*prediction value*/)); 337 338 DecisionTree.ContinuousEdge cedge = (DecisionTree.ContinuousEdge)edge; 339 DecisionTree.ContinuousNode cnode = (DecisionTree.ContinuousNode)dtree2.Root; 340 cnode.Graft((DecisionTree.BaseNode)cedge.NodeTo.Clone(), cedge.LeftBoundary, cedge.RightBoundary, cedge.Weight); 341 } 342 else 343 { 344 if (dtree2.Root.GetType() != typeof(DecisionTree.CategoricalNode)) 345 dtree2.Root.Replace(new DecisionTree.CategoricalNode(0, -1)); 346 347 DecisionTree.CategoricalEdge cedge = (DecisionTree.CategoricalEdge)edge; 348 DecisionTree.CategoricalNode cnode = (DecisionTree.CategoricalNode)dtree2.Root; 349 cnode.Graft((DecisionTree.BaseNode)cedge.NodeTo.Clone(), cedge.AcceptableCategories, cedge.Weight); 350 } 351 } 352 353 dtree2.Save("tree_reconstructed.xml"); 354 } 355 } 356 357 static void ADDispTree(DecisionTree.BaseNode node, String depthTabs = "") 358 { 359 DecisionTree.BaseEdge edge = node.ParentEdge; 360 361 Console.Write(depthTabs); 362 if (edge == null) 363 Console.Write("Root:"); 364 else 365 { 366 Console.Write("Edge: "); 367 if (edge is DecisionTree.ContinuousEdge) 368 { 369 DecisionTree.ContinuousEdge cedge = (DecisionTree.ContinuousEdge)edge; 370 Console.Write($"Continuous range [{cedge.LeftBoundary},{cedge.RightBoundary});"); 371 } 372 else 373 { 374 DecisionTree.CategoricalEdge cedge = (DecisionTree.CategoricalEdge)edge; 375 Console.Write($"Categorical subset {{{String.Join(",", cedge.AcceptableCategories)}}});"); 376 } 377 } 378 379 Console.Write($" Node type {node} with prediction {node.Prediction};"); 380 if (node is DecisionTree.ContinuousNode) 381 Console.Write($" And further split by Factor[{((DecisionTree.ContinuousNode)node).FactorIndex}]"); 382 else if (node is DecisionTree.CategoricalNode) 383 Console.Write($" And further split by Factor[{((DecisionTree.CategoricalNode)node).FactorIndex}]"); 384 Console.WriteLine(""); 385 386 foreach (DecisionTree.BaseEdge subedge in node) 387 ADDispTree(subedge.NodeTo, depthTabs + " "); 388 } 389 } 390}