Vector Class |
The class of vector is intended to represent algebraic vectors. We consider a vector to be a one-dimensional array of numbers.
In most descriptions the following notation is used for the vector:
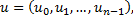
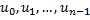 are called elements of the vector u. n is the size of the vector.
are called elements of the vector u. n is the size of the vector.
In the FinMath Library Vector class is intended to work with vectors. It provides plenty of constructors and methods for implementing operations on vectors.
Constructor | Description | Performance |
|---|---|---|
vector of zero size | ||
zero vector of the given size | ||
vector of the given size with all its elements set to the given value | ||
vector that contains elements copied from the array | ||
vector that contains elements copied from the other vector |
Constructor | Description | Performance |
|---|---|---|
vector of given size with elements uniformly distributed in [0; 1] | ||
vector of given size with elements that are sampled from the specified distribution | This method is very useful for creating a vector whose elements are distributed with some distribution. For example, we can use this method to create a vector with elements uniformly distributed in [-1, 1]. | |
vector that is a sample of given multivariate distribution | This method is useful for creating a vector that is distributed with a specified multivariate (or vector-variate) distribution. |
The example of Vector class usage:
1using System; 2using FinMath.LinearAlgebra; 3using FinMath.Statistics.Distributions; 4 5namespace FinMath.Samples 6{ 7 class BasicVectors 8 { 9 static void Main() 10 { 11- #region Constructing Vectors 12 13 // Way #1: no arguments. Creates a vector of length zero. 14 Vector v1 = new Vector(); 15 Console.WriteLine($"v1 = {v1}"); 16 17 // Way #1: specify the number of elements. All elements of 18 // are set to 0. 19 Vector v2 = new Vector(5); 20 Console.WriteLine($"v2 = {v2}"); 21 22 // Way #3: specify the number of elements and some value. All 23 // elements of the vector are set to the supplied value. 24 Vector v3 = new Vector(5, 1.0); 25 Console.WriteLine($"v3 = {v3}"); 26 27 // Way #4: specify the elements of the vector as a double 28 // array. The elements are copied to a storage area internal 29 // to the Vector. 30 Double[] elements = { 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0 }; 31 Vector v4 = new Vector(elements); 32 Console.WriteLine($"v4 = {v4}"); 33 34 // Way #5: specify the ealier created vector. The elements are 35 // copied to a storage area internal to the vector. 36 Vector v5 = new Vector(v4); 37 Console.WriteLine($"v5 = {v5}"); 38 39 // Way #6: specify the univariate distribution 40 Vector v6 = Vector.Random(5, new Normal(0.0, 5.0)); 41 Console.WriteLine($"v6 = {v6:F}"); 42 Console.WriteLine(); 43 44 #endregion 45 46- #region Vector Properties 47 48 // The Count property gives the number of elements of a Vector. 49 Console.WriteLine($"v2.Count = {v2.Count}"); 50 51 #endregion 52 53- #region Accessing Vector Elements 54 55 // The Vector class defines an indexer property that takes 56 // a zero-based index. 57 Console.WriteLine($"v2[2] = {v2[2]}"); 58 // You can assign to this property. 59 v2[2] = 9.0; 60 Console.WriteLine($"v2[2] = {v2[2]}"); 61 62 #endregion 63 } 64 } 65}


