Matrix Class |
The class of vector is intended to represent algebraic matrices. We consider a matrix to be a two-dimensional array of numbers.
In most descriptions the following notation is used for the matrix:
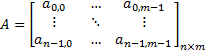
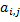 , i=0..n-1, j=0..m-1 are called elements of the matrix u. nxm is the size of the matrix.
, i=0..n-1, j=0..m-1 are called elements of the matrix u. nxm is the size of the matrix.
In the FinMath Library Matrix class is intended to work with matrices. It provides plenty of constructors and methods for implementing operations on matrices.
Property | Description | Performance |
|---|---|---|
columns | Number of columns in the matrix. | |
rows | Number of rows in the matrix. | |
size | Total number of elements in the matrix, i.e. the number of columns multiplied by the number of rows. | |
certain element by its index | Set or get an element of the matrix. |
Constructor | Description | Performance |
|---|---|---|
matrix with 0 columns and 0 rows | ||
zero matrix of the given order | ||
matrix of the given order with all its elements set to the given value | ||
zero matrix of the given size | ||
matrix of the given size with all its elements set to the given value | ||
matrix from multidimensional array | ||
a copy of the given matrix |
Constructor | Description | Performance |
|---|---|---|
identity matrix of the given order | ||
rectangular matrix with unit diagonal elements | ||
square matrix with given elements on the main diagonal | ||
rectangular matrix with given elements on the main diagonal | ||
square matrix with elements uniformly distributed in [0; 1] | ||
rectangular matrix with elements uniformly distributed in [0; 1] | ||
square matrix with elements which are samples from the specified univariate distribution | ||
rectangular matrix with elements which are samples from the specified univariate distribution | ||
matrix with elements which are samples from the specified multivariate distribution |
The example of Matrix class usage:
1using System; 2using FinMath.LinearAlgebra; 3using FinMath.Statistics.Distributions; 4 5namespace FinMath.Samples 6{ 7 class Program 8 { 9 static void Main() 10 { 11- #region Constructing Matrices 12 13 // Way #1: no arguments. Creates a matrix with 0 columns and 0 rows. 14 Matrix m1 = new Matrix(2); 15 Console.WriteLine($"m1 = {m1}"); 16 Console.WriteLine(); 17 18 // Way #1: specify the order. All elements are set to 0. 19 Matrix m2 = new Matrix(3); 20 Console.WriteLine($"m2 = {m2}"); 21 Console.WriteLine(); 22 23 // Way #3: specify the order. All elements are set to 10. 24 Matrix m3 = new Matrix(2, 10.0); 25 Console.WriteLine($"m3 = {m3}"); 26 Console.WriteLine(); 27 28 // Way #3: specify the size. All elements are set to 10. 29 Matrix m4 = new Matrix(2, 3, 10.0); 30 Console.WriteLine($"m4 = {m4}"); 31 Console.WriteLine(); 32 33 // Way #4: specify the elements of the vector as a double array. 34 Double[,] elements = { { 1.0, 2.0, 3.0 }, { 4.0, 5.0, 6.0 } }; 35 Matrix m5 = new Matrix(elements); 36 Console.WriteLine($"m5 = {m5}"); 37 Console.WriteLine(); 38 39 // Way #5: specify a univariate distribution 40 Matrix m6 = Matrix.Random(2, 3, new Normal(0.0, 5.0)); 41 Console.WriteLine($"m6 = {m6:F}"); 42 Console.WriteLine(); 43 44 // Way #5: specify a multivariate distribution 45 Matrix m7 = Matrix.Random(new MatrixNormal(2, 3)); 46 Console.WriteLine($"m7 = {m7:F}"); 47 Console.WriteLine(); 48 49 #endregion 50 51- #region Matrix Properties 52 53 // The size property 54 Console.WriteLine($"m2.Size = {m2.Size}"); 55 Console.WriteLine(); 56 57 // The rows property 58 Console.WriteLine($"m2.Rows = {m2.Rows}"); 59 Console.WriteLine(); 60 61 #endregion 62 63- #region Accessing Matrix Elements 64 65 // The Matrix class defines an indexer property that takes 66 // a zero-based index. 67 Console.WriteLine($"m2[2,0] = {m2[2, 0]}"); 68 Console.WriteLine(); 69 // You can assign to this property. 70 m2[2, 0] = 9.0; 71 Console.WriteLine($"m2[2,0] = {m2[2, 0]}"); 72 Console.WriteLine(); 73 74 #endregion 75 } 76 } 77}


