QR Decomposition |
In linear algebra QR decomposition is a decomposition of real matrix into the product of a unitary matrix Q and upper triangular (or upper trapezoidal) matrix R.
This topic contains the following sections:
Any real matrix A may be decomposed as:
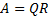
where R is an upper triangular (or upper trapezoidal) matrix and Q is a unitary matrix:
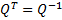
QR decomposition with column pivoting introduces a permutation matrix P:
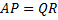
Column pivoting is useful when A is (nearly) rank deficient, or is suspected of being so. It can also improve numerical accuracy.
Constructors initialize a new instance of QR factorization of the given matrix.
Constructor | Description | Performance |
|---|---|---|
pass the data matrix | User specifies a matrix to factorize as a parameter. | |
use column pivoting | The boolean flag indicates whether to use column pivoting or not. In case of this constructor data matrix is unspecified, therefore user needs to use Update(Matrix data) method after initializing the factorization instance to set the matrix to factorize. | use column pivoting and set data matrix | The boolean flag indicates whether to use column pivoting or not. |
This method group includes getting decomposition matrices, updating data matrix and calculating permutation.
Operation | Description | Performance |
|---|---|---|
update data matrix | Computes the QR factorization of the given matrix. | |
R matrix | Returns the upper triangular (upper trapezoidal) matrix R. | |
Q matrix | Returns the unitary matrix Q. | |
economy-size R matrix | Returns the economy-size upper triangular matrix L. For example if we have QR decomposition like the following: 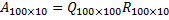 Thus matrix R is upper trapezoidal we can remove the lower 90 zero rows from matrix R and remove 90 columns from matrix Q. Such decomposition remains valid, but matrix Q will be no longer unitary, only it's columns will be orthogonal: 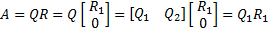 | |
economy-size Q matrix | Computes the economy-size matrix Q with orthogonal columns (see the description above). | |
permutation matrix | Computes the permutation matrix. | |
permutation | Computes the permutation of columns applied to matrix A (it is an integer array). | |
inversed permutation | Computes the inversed permutation of columns applied to matrix A (it is an integer array). | |
is full rank | Checks whether the matrix has full rank. |
This method group includes solving system of linear equations.
Operation | Description | Performance |
|---|---|---|
solve system of matrix equations | Solves a system of linear equations AX = B, where A is our data matrix and B and X are matrices. Returning result:Out of place: | |
solve system of linear equations | Solves a system of linear equations Ax = b, where A is our data matrix and b and x are vectors. Returning result:Out of place: |
The example of QR class usage:
1using System; 2using FinMath.LinearAlgebra; 3using FinMath.LinearAlgebra.Factorizations; 4 5namespace FinMath.Samples 6{ 7 class QRFactorization 8 { 9 static void Main() 10 { 11 // Generate random rectangular matrix. 12 Matrix A = Matrix.Random(4, 2); 13 Console.WriteLine("A = "); 14 Console.WriteLine(A.ToString("0.000")); 15 Console.WriteLine(); 16 17 // Perform QR factorization. 18 QR qr = new QR(A, false); 19 20 // Print matrix Q. 21 Console.WriteLine("Q = "); 22 Console.WriteLine(qr.Q().ToString("0.000")); 23 Console.WriteLine(); 24 25 // Print matrix R. 26 Console.WriteLine("R = "); 27 Console.WriteLine(qr.R().ToString("0.000")); 28 Console.WriteLine(); 29 30 // Disperancy of factorization. 31 Console.WriteLine($"Norm(A - Q * R) = {(A - qr.Q() * qr.R()).L2Norm():E8}"); 32 Console.WriteLine(); 33 34 // Print economic matrix Q. 35 Console.WriteLine("Economic Q = "); 36 Console.WriteLine(qr.EconomicQ().ToString("0.000")); 37 Console.WriteLine(); 38 39 // Print economic matrix R. 40 Console.WriteLine("Economic R = "); 41 Console.WriteLine(qr.EconomicR().ToString("0.000")); 42 Console.WriteLine(); 43 44 // Disperancy of economic factorization. 45 Console.WriteLine($"Norm(A - Q * R) = {(A - qr.EconomicQ() * qr.EconomicR()).L2Norm():E8}"); 46 Console.WriteLine(); 47 48 // Generate overdetermined system of linear equation and solve it. 49 Vector B = A * Vector.Random(2); 50 Vector X = qr.Solve(B); 51 52 // Print found solution. 53 Console.WriteLine("X = "); 54 Console.WriteLine(X.ToString("0.000")); 55 Console.WriteLine(); 56 57 // Print error. 58 Console.WriteLine($"Error = {(B - A * X).L2Norm():E8}"); 59 } 60 } 61}
