Kolmogorov Smirnov Two Sample Test |
Two sample Kolmogorov–Smirnov test of the null hypothesis that data in the samples are random samples from equal distributions, against the alternative that the distributions are different.
This topic contains the following sections:
The Kolmogorov–Smirnov test may also be used to test whether two underlying one-dimensional probability distributions differ. In this case, the Kolmogorov–Smirnov statistic is
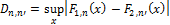
where F1,n and F2,n' are the empirical distribution functions of the first and the second sample respectively.
The null hypothesis is rejected at level α if
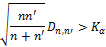
where Kα is found from
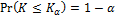
K is the random variable which has Kolmogorov distribution.
Note that the two-sample test checks whether the two data samples come from the same distribution. This does not specify what that common distribution is (e.g. normal or not normal).
The following constructors create an instance of KolmogorovSmirnovTest class.
Constructor | Description | Performance |
|---|---|---|
two-tailed test, default significance level | Constructor without parameters. Creates KolmogorovSmirnovTwoSampleTest instance with default significance level for two-tailed test. | |
default significance level | Creates KolmogorovSmirnovTwoSampleTest instance with default significance level and user defined tail. | |
two-tailed test, user defined significance level | Creates KolmogorovSmirnovTwoSampleTest instance for two-tailed test and user-defined significance level. | |
user defined tail and significance level | Creates KolmogorovSmirnovTwoSampleTest instance with user defined significance level and tail. |
The class provides the following methods:
Method | Description | Performance |
|---|---|---|
update | Updates test statistic using provided samples. User specifies two double array samples and offsets and number of elements to use in each sample: |
The class provides the following properties:
Property | Description | Performance |
|---|---|---|
region of acceptance | We fail to reject null hypothesis if test statistics is between left and right borders of region of acceptance. Region of acceptance left border: Region of acceptance right border: | |
p-value | The probability of obtaining a test statistic at least as extreme as the one that was actually observed, assuming that the null hypothesis is true. |
The example of KolmogorovSmirnovTest class usage:
1using System; 2using FinMath.LinearAlgebra; 3using FinMath.Statistics.HypothesisTesting; 4using FinMath.Statistics.Distributions; 5 6namespace FinMath.Samples 7{ 8 class KolmogorovSmirnovTwoSampleTestSample 9 { 10 static void Main() 11 { 12 //Create instances of normal distribution. 13 Normal distr1 = new Normal(0, 5); 14 Normal distr2 = new Normal(3, 5); 15 16 // Generate random series. 17 Vector series1 = Vector.Random(100, distr1); 18 Vector series2 = Vector.Random(150, distr2); 19 20 // Create an instance of KolmogorovSmirnovTwoSampleTest 21 KolmogorovSmirnovTwoSampleTest test = new KolmogorovSmirnovTwoSampleTest(0.05, Tail.Both); 22 test.Update(series1, series2); 23 24 Console.WriteLine("Test Result:"); 25 // Test decision 26 Console.WriteLine($" The null hypothesis failed to be rejected: {test.Decision}"); 27 // The statistic of KolmogorovSmirnovTwoSampleTest test. 28 Console.WriteLine($" Statistics = {test.Statistics:0.000}"); 29 // The p-value of the test statistic. 30 Console.WriteLine($" P-Value = {test.PValue:0.000}"); 31 32 } 33 } 34}

