Variance |
The Variance (Variance) (var) is a measurement of the spread between numbers in a data set relative to its mean. Variance is always non-negative: a small variance indicates that the data points tend to be very close to the mean value and hence to each other, while a high variance indicates that the data points are very spread out around the mean and from each other.
In the case of a set of N values 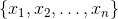 and the arithmetic mean
and the arithmetic mean 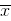 , the sample (unbiased) variance is
, the sample (unbiased) variance is
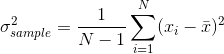
The population variance is differ only in division factor:
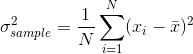
To initialize indicator, use one of the following constructors:
Variance – set default values: period = 14
Variance(Int32, Boolean) – set value for period
Variance(TimeSpan, Boolean) – sets time period
Use
Var - property to get current value
1// Create new instance 2var indicator = new Variance(28); 3 4// Number of stored values 5indicator.HistoryCapacity = 2; 6 7// Add new data point 8indicator.Add(CurrentPrice); 9 10// Get indicator value 11double IndicatorValue = indicator.Var; 12// Get previous value 13if (indicator.HistoryCount == 2) 14{ 15 double IndicatorPrevValue = indicator[1]; 16}