Cumulative Moving Average |
The Cumulative Moving Average (Cma) is also frequently called a running average or a long running average although the term running average is also used as synonym for a moving average.
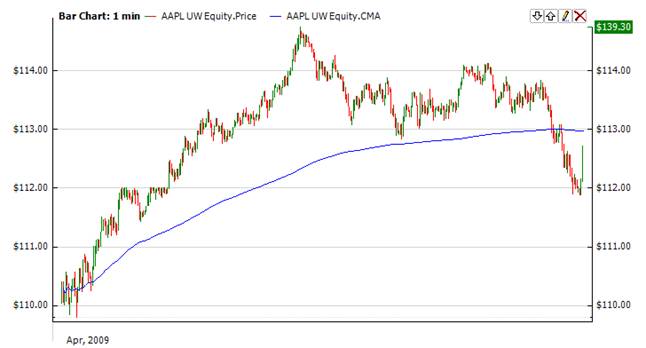
In some data acquisition systems, the data arrives in an orderly data stream and the statistician would like to calculate the average of all data up until the current data point, which in itself moves with time. For example, an investor may want the average price of all trades for a particular financial instrument up until the current time. As each new transaction occurs, the average price at the time of the transaction can be calculated for all transactions up to that point using the cumulative average.
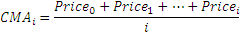
Indicator has no input parameters. To initialize Cma use the following constructor:
Use
CMA - property to get current value
1// Create new instance 2Cma cma = new Cma(); 3 4// Number of stored values 5cma.HistoryCapacity = 2; 6 7// Add new data point 8cma.Add(CurrentPrice, CurrentTime); 9 10// Get indicator value 11double IndicatorValue = cma.CMA; 12// Get previous value 13if (cma.HistoryCount == 2) 14{ 15 double IndicatorPrevValue = cma[1]; 16}