Exponential Moving Average |
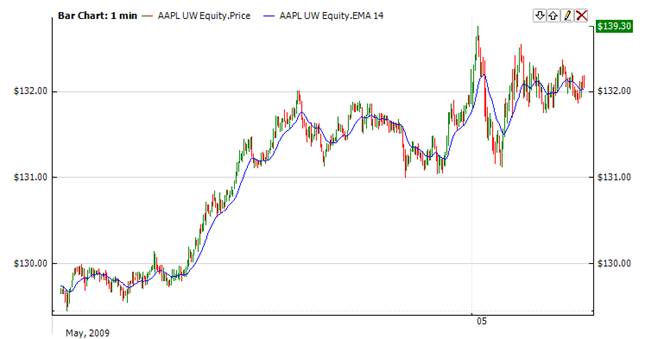
The Exponential Moving Average (Ema) is a staple of technical analysis and is used in countless technical indicators. In a Simple Moving Average, each value in the time period carries equal weight, and values outside of the time period are not included in the average. However, the Exponential Moving Average is a cumulative calculation, including all data. Past values have a diminishing contribution to the average, while more recent values have a greater contribution. This method allows the moving average to be more responsive to changes in the data.
Typically, the signal to buy comes in when the Ema crosses price from above. When Ema crosses price from below, it is a signal to sell.
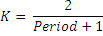
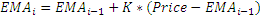
To initialize Exponential Moving Average indicator, use one of the following constructors:
Ema – set default values: period = 14
Ema(Int32) – set value for period
Ema(Double) – set value for factor (K in formula)
Use
EMA - property to get current value
1// Create new instance 2Ema ema = new Ema(28); 3 4// Number of stored values 5ema.HistoryCapacity = 2; 6 7// Add new data point 8ema.Add(CurrentPrice); 9 10// Get indicator value 11double IndicatorValue = ema.EMA; 12// Get previous value 13if (ema.HistoryCount == 2) 14{ 15 double IndicatorPrevValue = ema[1]; 16}