Standard Deviation |
The standard deviation (StandardDeviation) (std) is a statistic that measures the dispersion of a dataset relative to its mean and is calculated as the square root of the variance (Variance). Standard deviation is a statistical measurement in finance that, when applied to the annual rate of return of an investment, sheds light on the historical volatility of that investment. The greater the standard deviation of a security, the greater the variance between each price and the mean, which shows a larger price range.
In the case of a set of N values 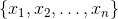 and the arithmetic mean
and the arithmetic mean 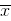 , the sample (unbiased) standard deviation is
, the sample (unbiased) standard deviation is
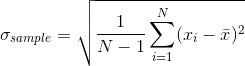
The population standard deviation is differ only in division factor:
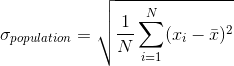
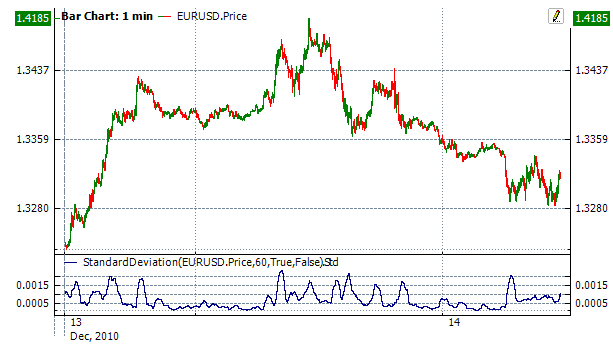
To initialize indicator, use one of the following constructors:
StandardDeviation – set default values: period = 14
StandardDeviation(Int32, Boolean) – set value for period
StandardDeviation(TimeSpan, Boolean) – sets time period
Use
Std - property to get current value
1// Create new instance 2var indicator = new StandardDeviation(28); 3 4// Number of stored values 5indicator.HistoryCapacity = 2; 6 7// Add new data point 8indicator.Add(CurrentPrice); 9 10// Get indicator value 11double IndicatorValue = indicator.Std; 12// Get previous value 13if (indicator.HistoryCount == 2) 14{ 15 double IndicatorPrevValue = indicator[1]; 16}